1. Introduction & Overview
What is Chargeback?
Chargeback is a financial mechanism used in IT and cloud computing to allocate costs of shared resources (e.g., cloud services, infrastructure, or tools) back to the departments, teams, or projects that consume them. In the context of DevSecOps, chargeback ensures accountability for resource usage while integrating cost management into the secure software development lifecycle (SDLC). It promotes transparency by tying costs to specific workloads, applications, or teams, ensuring that security practices do not inadvertently inflate budgets.
History or Background
Chargeback originated in traditional IT to track on-premises infrastructure costs (e.g., server usage, storage). With the rise of cloud computing in the early 2000s, chargeback became critical as organizations adopted pay-as-you-go models from providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. In DevSecOps, chargeback evolved to align with agile, automated, and security-focused workflows, ensuring teams balance rapid development with cost efficiency and compliance.
Why is it Relevant in DevSecOps?
- Cost Accountability: DevSecOps teams often deploy resources dynamically (e.g., containers, CI/CD pipelines). Chargeback ensures teams understand the financial impact of their security and development choices.
- Security Optimization: By tying costs to security tools (e.g., SAST/DAST scanners, monitoring services), chargeback encourages efficient use of resources without compromising security.
- Compliance and Governance: Chargeback supports compliance by tracking resource usage, ensuring alignment with budgets and regulatory requirements.
- Scalability: In cloud-native DevSecOps, chargeback helps manage costs as teams scale microservices, serverless functions, or Kubernetes clusters.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
- Chargeback: Allocating costs of shared IT resources to specific business units or teams based on usage.
- Showback: A non-billing variant of chargeback, where cost data is shared for visibility but not charged.
- Cost Allocation Tags: Metadata (e.g., AWS tags) used to categorize resources for tracking and billing.
- Cloud Cost Management: Tools and processes to monitor, optimize, and allocate cloud expenses.
- CI/CD Pipeline: Automated workflows in DevSecOps for building, testing, and deploying code, often consuming cloud resources.
- Shared Responsibility Model: In cloud environments, the division of security and cost responsibilities between provider and user.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Chargeback | Cost distribution method where expenses are billed to the team or project. |
| Showback | Similar to chargeback but only reports usage without actual billing. |
| FinOps | Financial Operations—a cultural practice to manage cloud cost collaboratively. |
| Unit Economics | Analysis of cost per unit of value delivered (e.g., per deployment). |
| Tagging | Assigning metadata to resources to associate them with cost centers. |
How Chargeback Fits into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
Chargeback integrates with DevSecOps across the SDLC:
- Planning: Define cost allocation strategies and tag policies for resources used in security and development.
- Development: Track costs of development environments (e.g., IDEs, test servers) and security tools (e.g., vulnerability scanners).
- Build/Test: Monitor CI/CD pipeline costs, including automated security testing (SAST, DAST).
- Deploy: Allocate costs for production environments, ensuring security controls (e.g., WAF, monitoring) are cost-effective.
- Monitor: Use chargeback data to optimize resource usage and detect anomalies (e.g., excessive security scanning costs).
| Phase | Chargeback Role |
|---|---|
| Plan | Forecasting and budgeting based on expected workloads. |
| Develop | Encouraging cost-aware coding and resource allocation. |
| Build/Test | Tracking CI/CD resource usage for testing environments. |
| Release | Cost validation during artifact deployment. |
| Operate | Real-time usage monitoring, cost reporting, alerting. |
| Monitor | Auditing and historical analysis of spend. |
3. Architecture & How It Works
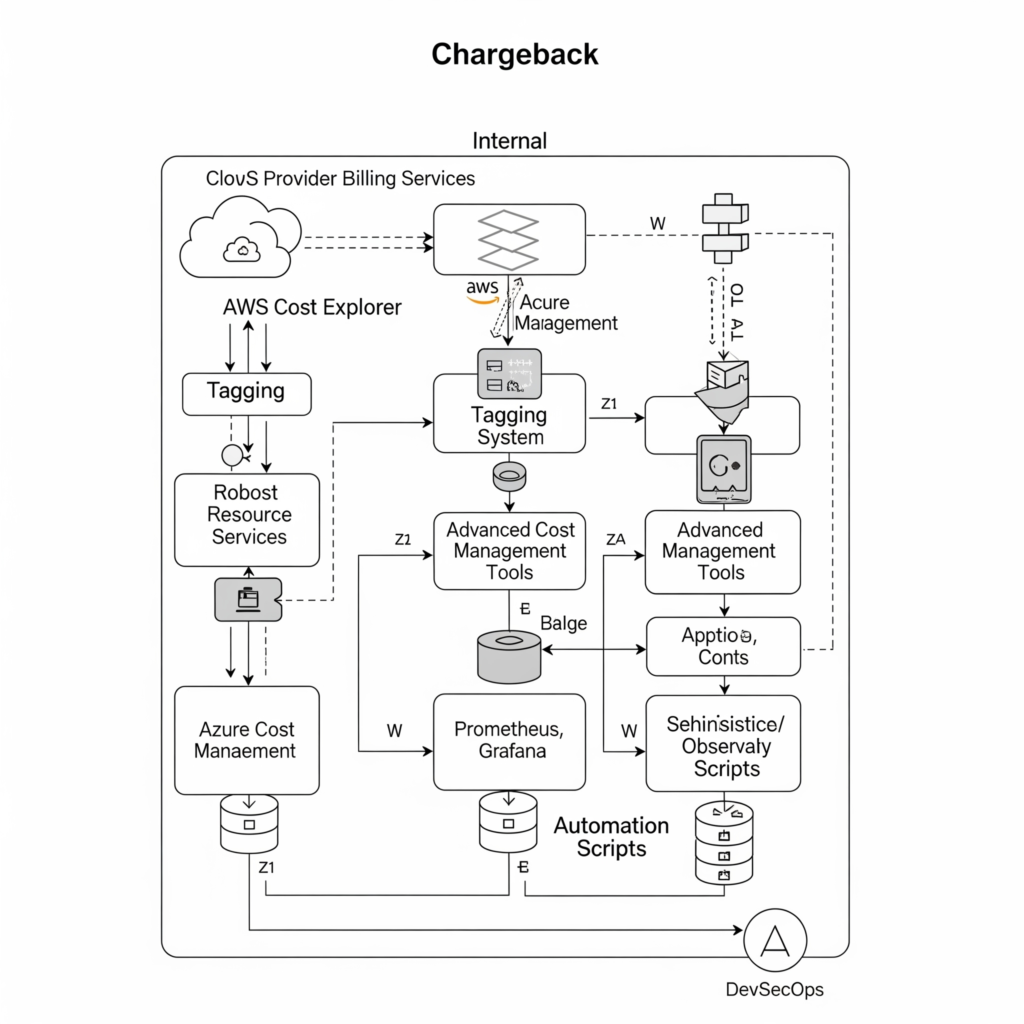
Components
- Cloud Provider Billing Services: AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, Google Cloud Billing.
- Tagging System: Metadata labels (e.g., “Team: DevSecOps”, “Project: App1”) to track resource usage.
- Cost Management Tools: Third-party tools like CloudHealth, Cloudability, or open-source Kubecost for Kubernetes.
- Monitoring/Observability: Tools like Splunk or Prometheus to correlate cost with security events.
- Automation Scripts: Scripts to enforce tagging and generate chargeback reports.
Internal Workflow
- Resource Tagging: Apply tags to all cloud resources (e.g., EC2 instances, S3 buckets) during provisioning.
- Cost Tracking: Cloud billing services aggregate costs by tags, linking usage to teams or projects.
- Report Generation: Automated reports detail costs for DevSecOps pipelines, security tools, and environments.
- Feedback Loop: Share cost data with teams to optimize resource usage and security practices.
Architecture Diagram Description
Imagine a diagram with:
- Left: Cloud resources (EC2, S3, Kubernetes) tagged with metadata (e.g., “Team: Security”).
- Center: CI/CD pipeline with security tools (SAST, DAST) consuming tagged resources.
- Right: Billing service (e.g., AWS Cost Explorer) feeding data to a cost management tool, generating chargeback reports.
- Bottom: DevSecOps teams receiving reports, adjusting workflows for cost and security efficiency.
+----------------+ +------------------+ +-------------------+
| CI/CD Pipelines| ---> | Tagging Engine | ---> | Metering Agent |
+----------------+ +------------------+ +-------------------+
↓
+-------------------+
| Cost Analyzer |
+-------------------+
↓
+--------------------+
| Chargeback Engine |
+--------------------+
↓
+-------------------+
| Dashboard/API |
+-------------------+
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: Integrate chargeback with Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions to track pipeline resource usage.
- Cloud Tools: Use AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management APIs to pull cost data into DevSecOps dashboards.
- IaC (Infrastructure as Code): Enforce tagging in Terraform or CloudFormation scripts for consistent cost tracking.
- Monitoring: Correlate cost spikes with security events using tools like Splunk or Datadog.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Cloud Account: Access to AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud with billing permissions.
- Tagging Policy: Define a tagging strategy (e.g., tags for team, project, environment).
- Cost Management Tool: Install a tool like CloudHealth or Kubecost (for Kubernetes).
- IAM Permissions: Ensure DevSecOps teams have read-only access to billing data.
- Scripting Environment: Python or Bash for automation scripts.
Hands-On: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
This example uses AWS Cost Explorer to set up chargeback for a DevSecOps team.
- Enable Cost Explorer:
- Log in to the AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Billing and Cost Management > Cost Explorer.
- Enable Cost Explorer (may take 24 hours to activate).
- Define Tags:
- Go to AWS Resource Groups > Tag Editor.
- Create tags, e.g.,
Team: DevSecOps,Environment: Dev,Project: App1. - Apply tags to resources (EC2, S3, etc.) manually or via IaC.
- Automate Tagging with Terraform:
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-12345678"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
tags = {
Team = "DevSecOps"
Environment = "Dev"
Project = "App1"
}
}4. Set Up Cost Explorer Report:
- In Cost Explorer, create a report filtering by tags (e.g.,
Team: DevSecOps). - Save the report for weekly/monthly distribution.
5. Automate Chargeback Reports:
import boto3
client = boto3.client('ce')
response = client.get_cost_and_usage(
TimePeriod={'Start': '2025-05-01', 'End': '2025-05-31'},
Granularity='MONTHLY',
Filter={'Tags': {'Key': 'Team', 'Values': ['DevSecOps']}},
Metrics=['UnblendedCost']
)
print(response['ResultsByTime'])- Run this script in a Lambda function or CI/CD pipeline to generate reports.
6. Share Reports: Distribute reports via email or integrate with Slack/Teams for DevSecOps visibility.
5. Real-World Use Cases
Use Case 1: CI/CD Pipeline Cost Tracking
A fintech company uses Jenkins for CI/CD with SAST/DAST tools. By tagging pipeline resources (Team: FintechDev, Pipeline: Security), they allocate costs to the DevSecOps team, identifying high-cost security scans and optimizing tool usage.
Use Case 2: Kubernetes Cost Allocation
A healthcare organization runs Kubernetes clusters for patient data apps. Using Kubecost, they track costs by namespace (Team: HealthSecOps), ensuring compliance with HIPAA while managing budget for security tools like Falco.
Use Case 3: Multi-Team Cloud Environment
An e-commerce platform uses AWS for multiple DevSecOps teams. Chargeback tags (Project: Checkout, Project: Inventory) help allocate S3 and EC2 costs, ensuring teams optimize security configurations (e.g., WAF rules) without overspending.
Use Case 4: Compliance Auditing
A government contractor uses chargeback to track costs of security tools (e.g., Splunk, Qualys) for compliance with NIST 800-53. Cost data ensures budget alignment and auditability, supporting DevSecOps governance.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Transparency: Teams see the financial impact of their DevSecOps practices, fostering accountability.
- Cost Optimization: Identifies high-cost security tools or misconfigured resources, reducing waste.
- Compliance Support: Tracks resource usage for audits, aligning with standards like GDPR, HIPAA.
- Scalability: Scales with cloud-native DevSecOps environments, supporting microservices and containers.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Tagging Overhead: Requires consistent tagging across all resources, which can be complex in large environments.
- Tool Costs: Third-party cost management tools (e.g., CloudHealth) add expenses.
- Cultural Resistance: Teams may resist cost accountability, viewing it as micromanagement.
- Accuracy Issues: Inaccurate tagging leads to flawed chargeback data, affecting decision-making.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Tagging complexity | Requires consistent tag strategy. |
| Inaccurate cost estimation | Without real-time billing data. |
| Tool overhead | Some solutions like Kubecost have resource cost. |
| Cultural resistance | Developers may resist financial accountability. |
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Enforce mandatory tagging policies using IAM conditions or AWS Organizations.
- Use automated SAST/DAST tools to balance security and cost, avoiding manual overprovisioning.
- Monitor cost anomalies with tools like AWS Budgets to detect potential security misconfigurations.
Performance and Maintenance
- Regularly review chargeback reports to identify unused resources (e.g., idle EC2 instances).
- Automate tag enforcement with IaC tools like Terraform or CloudFormation.
- Integrate cost data with observability tools (e.g., Prometheus) for real-time insights.
Compliance Alignment
- Map chargeback data to compliance frameworks (e.g., NIST, ISO 27001) for audit readiness.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict billing data access to authorized DevSecOps members.
Automation Ideas
- Automate chargeback reports with AWS Lambda or Azure Functions.
- Use Kubernetes cost allocation tools like Kubecost for containerized workloads.
- Implement “break the build” policies in CI/CD if untagged resources are detected.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Aspect | Chargeback | Showback | No Cost Allocation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Allocates costs to teams, often with billing | Shares cost data without billing | No cost tracking or allocation |
| Use Case | Budget accountability, compliance audits | Cost visibility, team awareness | Small teams, low-budget environments |
| Pros | Enforces accountability, supports compliance | Promotes transparency, less resistance | Simple, no overhead |
| Cons | Tagging complexity, cultural pushback | No financial accountability | No visibility into resource usage |
| Best for | Large DevSecOps teams, regulated industries | Early-stage cost awareness | Small, non-complex projects |
When to Choose Chargeback
- Use chargeback in regulated industries (e.g., finance, healthcare) where cost tracking aligns with compliance.
- Choose showback for organizations transitioning to DevSecOps, focusing on visibility without immediate billing.
- Avoid chargeback in small teams where tagging overhead outweighs benefits.
| Tool | Focus | When to Use |
|---|---|---|
| Kubecost | Kubernetes-native | For detailed k8s chargeback |
| CloudHealth | Enterprise FinOps | For multi-cloud cost management |
| AWS Cost Explorer | AWS-only | For single cloud, native AWS environments |
9. Conclusion
Chargeback in DevSecOps bridges cost management with secure software development, ensuring teams balance agility, security, and budget. By integrating cost allocation into the SDLC, organizations achieve transparency, optimize resources, and meet compliance requirements. As cloud adoption grows, chargeback will evolve with AI-driven cost analytics and tighter integration with DevSecOps tools.