Table of Contents
- Introduction & Overview
- Core Concepts & Terminology
- Architecture & How It Works
- Installation & Getting Started
- Real-World Use Cases
- Benefits & Limitations
- Best Practices & Recommendations
- Comparison with Alternatives
- Conclusion
1. Introduction & Overview
What is Cost Optimization?
Cost optimization in DevSecOps is the process of minimizing expenses in development, security, and operations while maintaining performance, security, and reliability. It involves analyzing resource usage, automating processes, and leveraging tools to reduce waste in cloud infrastructure, CI/CD pipelines, and security practices.
History or Background
Cost optimization became critical with the rise of cloud computing in the early 2000s, driven by platforms like AWS, Azure, and GCP. The adoption of DevOps, and later DevSecOps, which integrates security into the development lifecycle, highlighted the need to balance agility, security, and cost. Frameworks like AWS Well-Architected and FinOps emerged to address escalating cloud costs.
Why is it Relevant in DevSecOps?
Cost optimization is essential in DevSecOps for:
- Scalability: Dynamic resource allocation in pipelines can lead to overspending if not managed.
- Security Integration: Security tools are resource-intensive, requiring cost management.
- Operational Efficiency: Aligns with DevSecOps’ focus on automation and efficiency.
- Compliance: Ensures responsible resource use, reducing audit risks.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
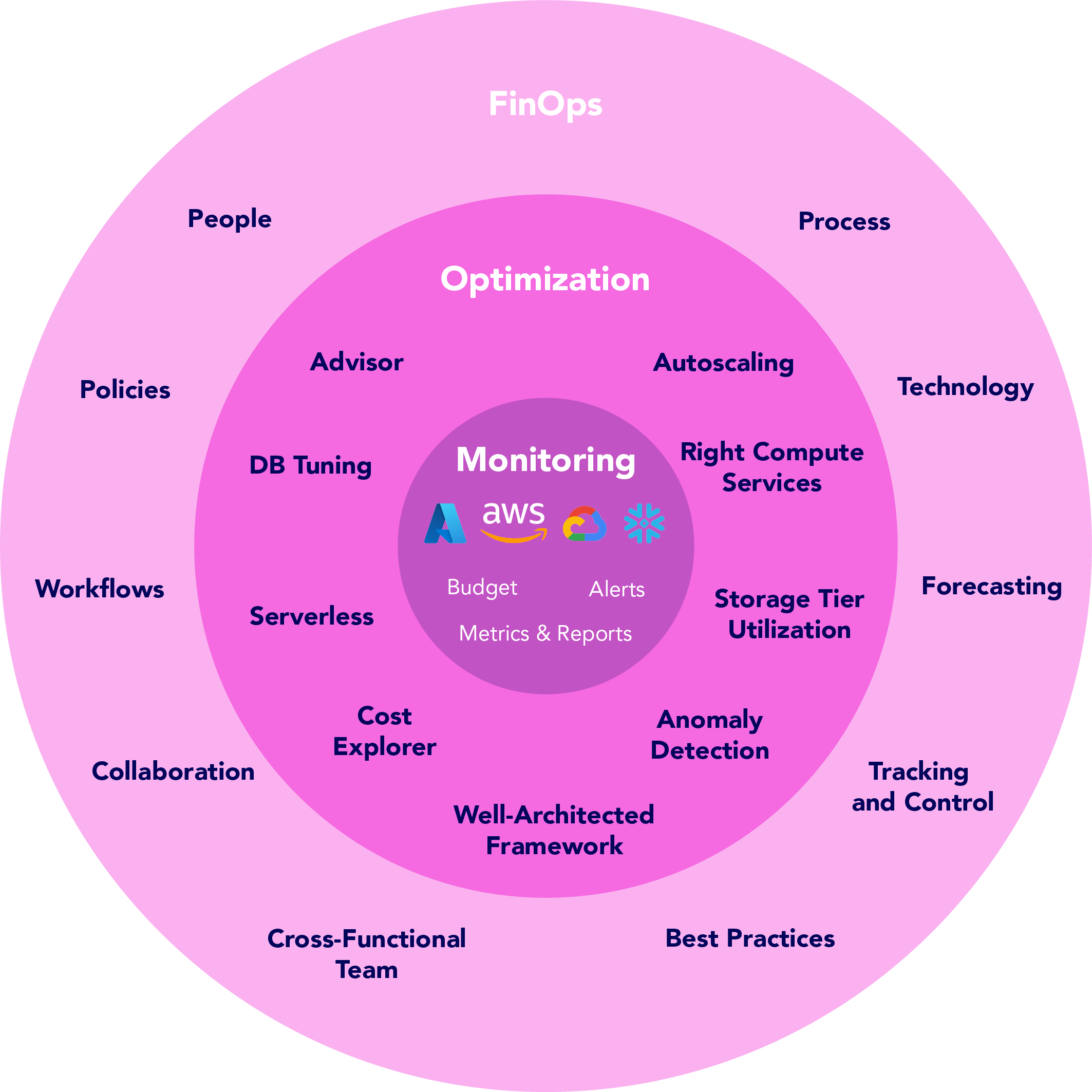
- FinOps: A practice combining financial accountability with cloud operations to optimize costs.
- Resource Tagging: Labeling cloud resources for tracking and cost allocation.
- Auto-Scaling: Automatically adjusting compute resources based on demand.
- Cost Allocation: Assigning costs to specific teams, projects, or applications.
- Serverless: A model where cloud providers manage infrastructure, billing only for usage.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| FinOps | Financial Operations, integrating finance and engineering to manage cloud costs. |
| Cost Anomaly Detection | Detecting unexpected cost spikes automatically. |
| Tagging/Labeling | Adding metadata to resources to track costs per team, project, or environment. |
| Idle Resource Detection | Identifying underutilized or unused cloud resources. |
| RI/SP Management | Managing Reserved Instances/Savings Plans in cloud to reduce cost. |
| Showback/Chargeback | Mechanisms to attribute and report cost usage back to teams. |
How it Fits into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
Cost optimization integrates across DevSecOps stages:
- Plan: Define cost policies and budgets.
- Code: Use cost-efficient tools for development and testing.
- Build: Optimize CI/CD pipelines to reduce resource usage.
- Test: Leverage serverless or containerized testing environments.
- Release/Deploy: Use auto-scaling and reserved instances.
- Operate: Monitor costs with tools like AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management.
- Monitor: Implement continuous cost monitoring and anomaly detection.
Plan → Develop → Build → Test → Release → Deploy → Operate → Monitor
↑ ↑ ↑
Cost gates in CI Cost guardrails Anomaly alerts
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components and Internal Workflow
Cost optimization involves:
- Cloud Cost Management Tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, or Google Cloud Billing.
- Monitoring Systems: Prometheus, Grafana, or CloudWatch for usage tracking.
- Automation Scripts: Scripts to shut down unused resources or optimize instance types.
- Tagging Strategies: Metadata for cost allocation.
Workflow: Identify resources, analyze usage, apply optimizations (e.g., right-sizing instances), and monitor continuously.
Architecture Diagram Description
The architecture includes:
- A cloud provider (e.g., AWS) hosting compute (EC2), storage (S3), and CI/CD services (CodePipeline).
- A monitoring layer (CloudWatch) feeding data to a cost management tool (AWS Cost Explorer).
- Automation scripts adjusting resources via APIs (e.g., shutting down idle instances).
- A dashboard displaying cost metrics, tagged by team/project.
Developer Commit
|
CI/CD Pipeline ─────► Cost Plugin (e.g., Infracost) ─────► Cloud Cost API
| |
└─► Security Scan & Cost Gate ▼
Alerts & Dashboards (Grafana, CloudHealth)Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD Pipelines: Integrate cost checks in Jenkins or GitLab to flag expensive builds.
- Cloud APIs: Use AWS SDK or Azure CLI for automation.
- Container Orchestration: Kubernetes with Cluster Autoscaler to optimize pod usage.
- Security Tools: Integrate cost-efficient security scanning (e.g., Snyk, OWASP ZAP) into pipelines.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Cloud account (AWS, Azure, or GCP) with billing access.
- Basic knowledge of DevSecOps tools (e.g., Jenkins, Docker, Kubernetes).
- Install AWS CLI or Azure CLI for automation.
- Enable cost monitoring tools (e.g., AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management).
Hands-on: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
Here’s how to set up cost optimization using AWS:
- Enable AWS Cost Explorer:
aws ce enable-cost-explorer- Set Up Resource Tagging:
Create a tagging policy in AWS:
{
"TagPolicies": [
{
"Key": "Project",
"Values": ["App1", "App2"]
},
{
"Key": "Environment",
"Values": ["Dev", "Prod"]
}
]
}- Configure Auto-Scaling:
Set up an auto-scaling group in AWS EC2:
aws autoscaling create-auto-scaling-group \
--auto-scaling-group-name my-asg \
--launch-template LaunchTemplateName=my-template \
--min-size 1 --max-size 3- Set Up Cost Alerts:
Create a budget in AWS Budgets:
aws budgets create-budget \
--account-id 123456789012 \
--budget-name MyBudget \
--budget-limit Amount=100 Unit=USD- Monitor Costs:
Use AWS Cost Explorer to visualize usage by tag.
5. Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Optimizing CI/CD Pipelines
A tech company uses Jenkins for CI/CD. By analyzing build logs, they identify test environments running 24/7. They implement a script to shut down test instances after hours, saving 30% on EC2 costs.
Scenario 2: Serverless Security Scanning
A fintech firm uses AWS Lambda for security scans in their pipeline. Switching to serverless reduces costs by 40% compared to dedicated EC2 instances, as Lambda bills only for execution time.
Scenario 3: Kubernetes Cost Optimization
An e-commerce company uses Kubernetes. They implement Cluster Autoscaler and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler, reducing node usage by 25% during low-traffic periods.
Scenario 4: Industry-Specific Example (Healthcare)
A healthcare provider uses Azure for patient data processing. By right-sizing VMs and using Azure Reserved Instances, they save 20% annually while maintaining HIPAA compliance.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Cost Savings: Eliminates waste to reduce cloud bills.
- Scalability: Aligns resources with demand.
- Transparency: Tagging and monitoring improve cost visibility.
- Compliance: Ensures responsible resource use for audits.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Complexity: Requires expertise in cloud and DevSecOps tools.
- Initial Setup Time: Tagging and automation setup can be time-consuming.
- Over-Optimization Risk: Excessive cost-cutting may impact performance or security.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Use least-privilege IAM roles for cost management tools.
- Encrypt cost data in transit and at rest.
Performance and Maintenance
- Regularly review cost reports to identify anomalies.
- Automate resource cleanup using scripts or tools like AWS Lambda.
Compliance Alignment and Automation Ideas
- Align with frameworks like NIST or ISO 27001 by documenting cost policies.
- Use Infrastructure as Code (IaC) with Terraform to enforce cost-efficient configurations:
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-12345678"
instance_type = "t3.micro" # Cost-efficient instance
tags = {
Project = "App1"
}
}8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Approach | Pros | Cons | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| FinOps | Comprehensive, team-focused | Requires cultural shift | Large enterprises |
| Cloud-Native Tools | Easy integration | Vendor lock-in | Single-cloud setups |
| Third-Party Tools (e.g., CloudHealth) | Advanced analytics | Additional cost | Multi-cloud environments |
| Manual Optimization | Low setup cost | Time-intensive | Small teams |
When to Choose Cost Optimization in DevSecOps:
Use when integrating security and automation is critical, and you need to balance agility with cost control. Choose manual optimization for small-scale projects with limited budgets.
9. Conclusion
Cost optimization in DevSecOps aligns development, security, and operations with financial efficiency. By leveraging cloud tools, automation, and best practices, organizations can reduce costs while maintaining robust pipelines. Future trends include AI-driven cost predictions and deeper FinOps integration.