1. Introduction & Overview
What is Budget Policy in DevSecOps?
Budget policy in the context of DevSecOps refers to the strategic framework and practices for managing financial resources allocated to development, security, and operations processes within a software development lifecycle (SDLC). It involves defining, enforcing, and monitoring cost-related policies to ensure efficient resource utilization while maintaining security and operational integrity. Budget policies in DevSecOps focus on optimizing cloud spending, tool licensing, infrastructure costs, and personnel expenses while aligning with security and compliance requirements.
History or Background
The concept of budget policy in DevSecOps emerged as organizations increasingly adopted cloud-native technologies and DevOps practices. Historically, IT budgeting was siloed, with separate budgets for development, operations, and security. The rise of DevSecOps in the late 2010s, driven by the need for faster and more secure software delivery, necessitated a unified approach to budgeting. Tools like cloud cost management platforms and policy-as-code frameworks, such as Terraform and Open Policy Agent (OPA), began integrating financial governance into DevSecOps pipelines to address escalating cloud costs and compliance demands.
Why is it Relevant in DevSecOps?
Budget policy is critical in DevSecOps for several reasons:
- Cost Optimization: DevSecOps environments often rely on cloud infrastructure, where uncontrolled resource provisioning can lead to significant cost overruns.
- Security Alignment: Budget policies ensure that security tools and practices are adequately funded without compromising development velocity.
- Compliance and Governance: Enforcing budget policies as code aligns with regulatory requirements, ensuring auditable and repeatable financial controls.
- Collaboration: Budget policies foster collaboration between development, security, and operations teams by aligning financial goals with technical objectives.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
- Budget Policy: A set of rules defining acceptable spending limits, resource allocation, and cost monitoring within DevSecOps workflows.
- Policy as Code (PaC): Codifying budget policies using tools like OPA or Terraform to enforce cost controls programmatically.
- Cloud Cost Management: Tools and practices to monitor and optimize cloud spending, such as AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management.
- Cost Allocation Tags: Metadata applied to resources to track and categorize spending.
- Continuous Monitoring: Automated tracking of budget adherence in real-time across CI/CD pipelines.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Budget Threshold | Predefined spending limit at which alerts or actions are triggered. |
| Spending Guardrails | Enforced limits that prevent exceeding budget allocations. |
| Cost Anomaly Detection | Identifies unusual spending patterns through automation. |
| Budget Enforcement | Automatic actions (e.g., service throttling or halting deployments) when policies are violated. |
| Tags | Metadata labels (e.g., env:prod, team:security) used to apply budgets selectively. |
| Linked Accounts/Projects | Aggregation of billing data from multiple cloud accounts for centralized budgeting. |
How It Fits into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
Budget policy integrates into the DevSecOps lifecycle at multiple stages:
- Plan: Define budget constraints for projects, including tool licenses and cloud resources.
- Code: Embed cost policies in infrastructure-as-code (IaC) scripts to enforce limits during provisioning.
- Build: Use CI/CD pipelines to validate budget compliance before deployment.
- Test: Simulate resource usage to estimate costs and identify potential overruns.
- Deploy: Enforce policies to restrict deployment of costly or unapproved resources.
- Monitor: Continuously track spending against budgets using dashboards and alerts.
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components
- Policy Engine: Tools like OPA or HashiCorp Sentinel enforce budget policies programmatically.
- Cost Management Tools: Platforms like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, or third-party tools (e.g., CloudHealth) provide visibility into spending.
- CI/CD Integration: Tools like Jenkins or GitLab integrate budget checks into pipelines.
- Monitoring Dashboards: Visual tools for real-time cost tracking and alerts.
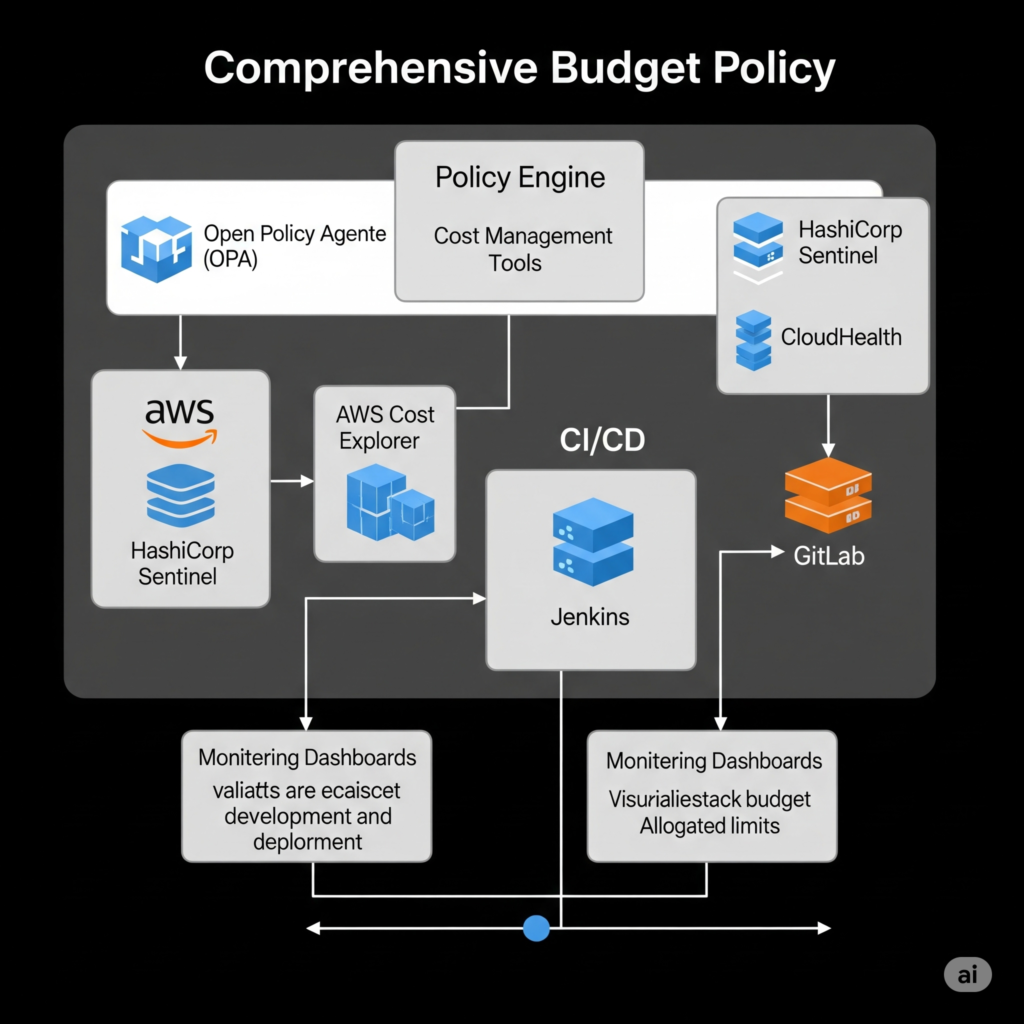
Internal Workflow
- Policy Definition: Budget policies are defined as code (e.g., Rego for OPA) specifying limits on resource types, regions, or spending thresholds.
- Policy Enforcement: Policies are applied during IaC provisioning or CI/CD runs to block non-compliant resources.
- Cost Monitoring: Real-time tracking of resource usage against budgets, with alerts for anomalies.
- Audit and Reporting: Logs and reports are generated for compliance and financial audits.
Architecture Diagram Description
The architecture consists of:
- Input Layer: IaC templates (e.g., Terraform) defining infrastructure.
- Policy Layer: OPA or Sentinel evaluating budget compliance.
- CI/CD Pipeline: Jenkins or GitLab integrating policy checks.
- Cloud Provider: AWS, Azure, or GCP providing cost data via APIs.
- Monitoring Layer: Dashboards (e.g., Grafana) displaying spending metrics.
+-----------------+ +-------------------+
| Developer/DevOps| ---> | Budget Policy YAML|
+-----------------+ +-------------------+
|
v
+-----------+
| CI/CD Tool|
| (Jenkins, |
| GitHub Actions) +------------------+
+-----------+ -----> | Cloud Cost APIs |
| | (AWS, GCP, Azure)|
| +------------------+
v
+------------+
| Enforcement|
| & Alerts |
+------------+
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: Budget checks are embedded as pipeline stages using plugins (e.g., Terraform Validator).
- Cloud Tools: APIs from AWS Cost Explorer or Azure Cost Management feed cost data into policy engines.
- Secrets Management: Tools like AWS Secrets Manager secure budget-related credentials.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Tools Required: Terraform, OPA, a cloud provider account (e.g., AWS), and a CI/CD tool (e.g., Jenkins).
- Access: Cloud provider credentials with permissions to access cost APIs.
- Environment: A development environment with Git installed for version control.
- Knowledge: Basic understanding of IaC and DevSecOps principles.
Hands-on: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
- Install Terraform and OPA:
# Install Terraform
wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/1.5.7/terraform_1.5.7_linux_amd64.zip
unzip terraform_1.5.7_linux_amd64.zip
sudo mv terraform /usr/local/bin/
# Install OPA
curl -L -o opa https://openpolicyagent.org/downloads/v0.55.0/opa_linux_amd64
chmod +x opa
sudo mv opa /usr/local/bin/- Set Up AWS Cost Explorer:
- Enable Cost Explorer in the AWS Management Console.
- Create an IAM role with
AWSCostExplorerReadOnlyAccesspermissions.
3. Define Budget Policy in OPA:
package budget_policy
default allow = false
allow {
input.resource_type == "AWS::EC2::Instance"
input.region == "us-east-1"
input.estimated_cost < 100
}Save as budget_policy.rego.
- Integrate with Terraform:
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}- Run Policy Check:
opa eval -i terraform_plan.json -d budget_policy.rego "data.budget_policy.allow"- Set Up CI/CD Integration:
- Add a Jenkins pipeline stage to run OPA checks:
groovy stage('Budget Policy Check') { steps { sh 'opa eval -i terraform_plan.json -d budget_policy.rego "data.budget_policy.allow"' } }
5. Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Cloud Cost Optimization
A fintech company uses budget policies to restrict deployment of expensive EC2 instances in non-approved regions, reducing cloud costs by 20% while maintaining compliance with PCI-DSS.
Scenario 2: Compliance Enforcement
A government agency integrates budget policies with OPA to ensure cloud spending aligns with federal regulations, automating audits and reducing manual oversight.
Scenario 3: Resource Tagging
An e-commerce platform enforces cost allocation tags via policies, enabling precise tracking of department-level spending and improving budget transparency.
Scenario 4: Startup Cost Control
A startup uses budget policies in CI/CD pipelines to cap resource provisioning, preventing unexpected cost spikes during rapid scaling.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Cost Efficiency: Prevents budget overruns by enforcing spending limits.
- Automation: Integrates cost checks into CI/CD, reducing manual effort.
- Compliance: Aligns with regulatory requirements through auditable policies.
- Collaboration: Encourages shared responsibility across Dev, Sec, and Ops teams.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Complexity: Setting up policy-as-code requires expertise in tools like OPA.
- False Positives: Overly strict policies may block legitimate resources.
- Tool Integration: Compatibility issues between cloud providers and policy engines.
- Cultural Resistance: Teams may resist additional budget checks, perceiving them as slowing development.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Use least privilege principles for cost API access.
- Encrypt sensitive budget data using tools like AWS Secrets Manager.
Performance
- Optimize policy evaluation by caching results in CI/CD pipelines.
- Use lightweight policy engines to minimize pipeline latency.
Maintenance
- Regularly update budget policies to reflect changing cloud pricing.
- Monitor policy effectiveness using metrics like cost savings and compliance rates.
Compliance Alignment
- Align policies with standards like NIST or OWASP for regulatory compliance.
- Automate audit logging for traceability.
Automation Ideas
- Implement auto-scaling policies to adjust resources based on budget thresholds.
- Use serverless functions to trigger cost alerts via Slack or email.
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Budget Policy with PaC | Manual Budget Tracking | Cloud Cost Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Automation | High | Low | Medium |
| CI/CD Integration | Seamless | None | Partial |
| Compliance Auditability | High | Low | Medium |
| Scalability | High | Low | High |
| Complexity | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
When to Choose Budget Policy
- Choose PaC: For organizations with mature DevSecOps practices needing automated, auditable budget controls.
- Choose Manual Tracking: For small teams with simple budgets and minimal cloud usage.
- Choose Cloud Cost Tools: For basic cost monitoring without deep CI/CD integration.
9. Conclusion
Budget policy in DevSecOps is a transformative approach to managing financial resources while ensuring security and operational efficiency. By integrating cost controls into the SDLC, organizations can optimize spending, enhance compliance, and foster collaboration. As cloud adoption grows, tools like OPA and cloud-native cost management platforms will drive future trends in budget policy automation.