1. Introduction & Overview
What is FinOps?
FinOps, or Cloud Financial Operations, is a framework that blends financial accountability with cloud management to optimize costs while maximizing business value. It fosters collaboration among finance, engineering, and business teams, ensuring transparency and data-driven decisions in cloud spending.
History or Background
FinOps emerged with the rise of cloud computing, as organizations struggled to manage variable cloud costs using traditional IT financial models. The FinOps Foundation, established in 2019 under the Linux Foundation, formalized the practice with defined principles and best practices, addressing the need for a dynamic approach to cloud cost management.
Why is it Relevant in DevSecOps?
DevSecOps integrates development, security, and operations for rapid, secure software delivery. FinOps enhances this by embedding cost management into the DevSecOps lifecycle, ensuring financial efficiency without compromising security or speed. This synergy, sometimes called DevSecFinOps, aligns cloud spending with security and performance goals, making it essential for modern cloud-native workflows.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
- FinOps: A practice combining finance, technology, and business to optimize cloud costs.
- Cloud Cost Management: Monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing cloud expenses.
- Cost Allocation: Assigning cloud costs to specific teams, projects, or workloads.
- Rightsizing: Matching cloud resources to workload demands to avoid overprovisioning.
- Unit Economics: Measuring cloud costs per business unit (e.g., cost per customer).
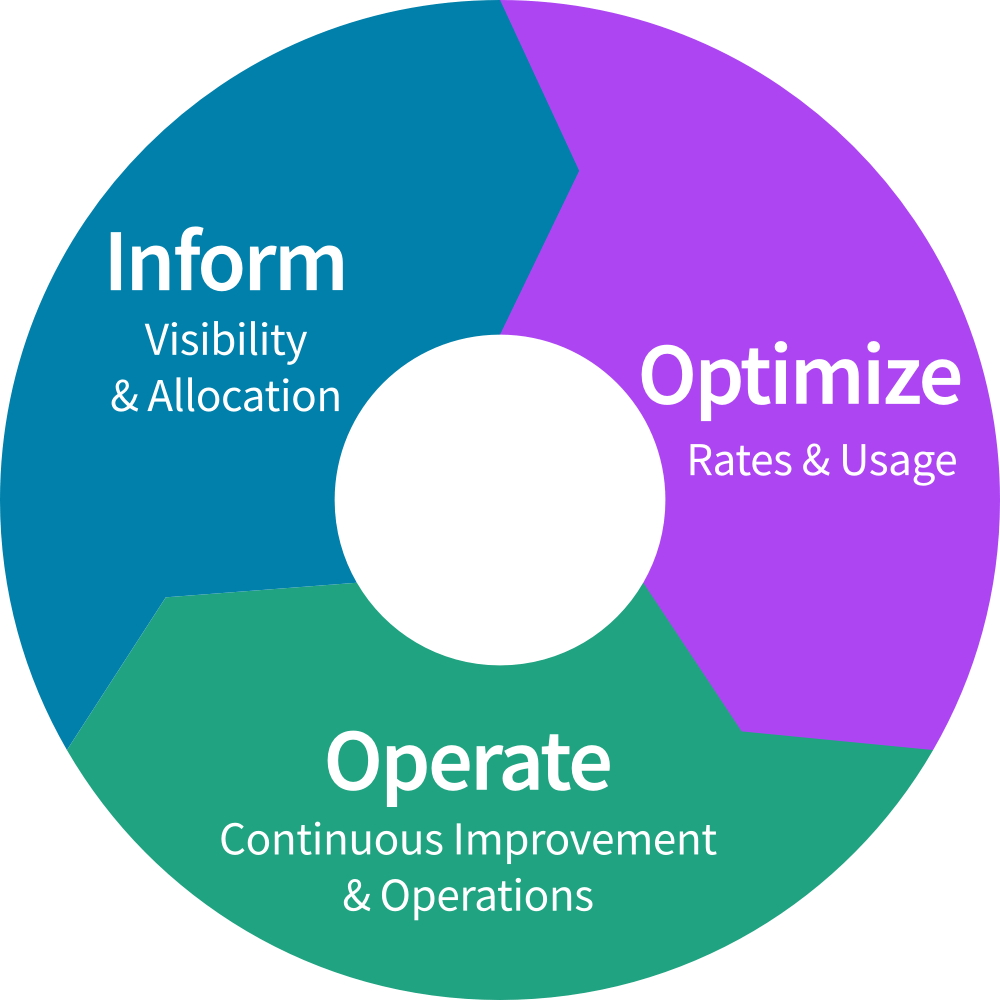
- Inform, Optimize, Operate: The three phases of the FinOps lifecycle.
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud Unit Economics | Measuring value (e.g., cost per transaction, per user) |
| Chargeback/Showback | Charging departments or showing cost usage |
| Tagging/Labeling | Adding metadata to resources for tracking costs |
| Commitment Discounts | Reserved instances or Savings Plans |
| Cost Anomaly Detection | Alerting when unexpected cost spikes occur |
| Rightsizing | Optimizing resource allocation to avoid waste |
How it Fits into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
FinOps integrates with DevSecOps at every stage:
- Plan: Incorporate cost considerations in architecture design.
- Code: Use cost-aware coding, e.g., serverless architectures.
- Build: Embed cost checks in CI/CD pipelines.
- Test: Evaluate cost impact of test environments.
- Release/Deploy: Optimize production resource allocation.
- Operate: Monitor and adjust cloud usage in real-time.
- Monitor: Use FinOps tools for continuous cost visibility.
| DevSecOps Phase | FinOps Role |
|---|---|
| Plan | Budget forecasting, cost estimation |
| Develop | Set cost-aware coding and infrastructure standards |
| Build | Integrate cost policies into CI tools |
| Test | Simulate workloads for cost benchmarking |
| Release | Review cloud bills before going live |
| Operate | Real-time cost monitoring and anomaly alerts |
| Monitor | Dashboarding and reporting per team or microservice |
This ensures cost efficiency aligns with security and agility.
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components and Internal Workflow
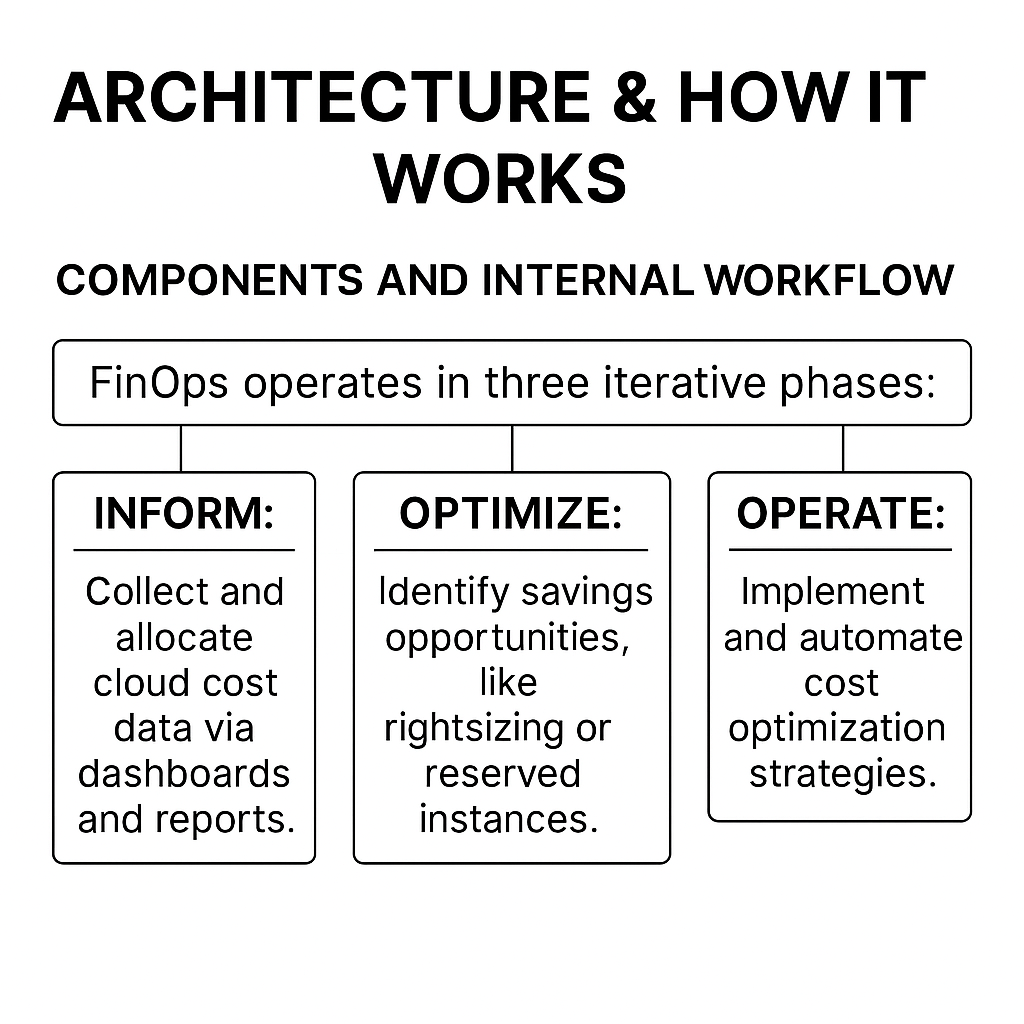
FinOps operates in three iterative phases:
- Inform: Collect and allocate cloud cost data via dashboards and reports.
- Optimize: Identify savings opportunities, like rightsizing or reserved instances.
- Operate: Implement and automate cost optimization strategies.
Key components include:
- FinOps teams (cross-functional groups).
- Cost management tools (e.g., CloudZero, Finout).
- Cloud provider-native tools (e.g., AWS Cost Explorer).
Architecture Diagram Description
The FinOps architecture can be visualized as:
- Top Layer (Governance): FinOps team sets policies, KPIs, and compliance.
- Middle Layer (Tools): Cost management platforms integrate with cloud providers (AWS, Azure, GCP) for data analysis.
- Bottom Layer (Infrastructure): Tagged cloud resources (compute, storage) feed cost data to tools.
Data flows from infrastructure to tools, providing insights to governance for iterative optimization.
[Cloud Providers]
↓
[Cost Export APIs (CUR, Azure Cost, GCP Billing)]
↓
[FinOps Platform]
├── Data Collector
├── Normalizer
├── Rule Engine (budgets, policies)
├── Visualization (Grafana, PowerBI)
└── CI/CD Integrations (Jenkins, GitHub Actions)
↓
[Stakeholders: DevOps, Finance, Security Teams]
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
FinOps integrates with:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Tools like Jenkins or GitLab trigger cost checks (e.g., Infracost for cost estimation).
- Cloud-Native Tools: AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, GCP Cost Management.
- Third-Party Tools: Cloudability, nOps for multi-cloud visibility.
| Tool | Integration |
|---|---|
| Terraform | Enforce tagging policies for cost tracking |
| Jenkins/GitLab | Add cost checks as a pipeline stage |
| Kubernetes | Cost breakdown per namespace or pod |
| Security Tools (e.g., Prisma, Falco) | Cross-reference cost and security anomalies |
Example: Infracost in GitHub Actions for cost estimation:
name: Cost Estimation
on: [pull_request]
jobs:
infracost:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: infracost/infracost-action@v1
with:
api-key: ${{ secrets.INFRACOST_API_KEY }}4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Cloud Account: Access to AWS, Azure, or GCP with billing permissions.
- FinOps Tool: Choose CloudZero, Finout, or native cloud cost tools.
- Tagging Strategy: Tag resources for cost allocation (e.g., by team, project).
- Team Structure: Form a cross-functional FinOps team (finance, engineering, security).
Hands-On: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
Set up AWS Cost Explorer with FinOps practices:
- Enable Cost Explorer:
- Log in to AWS Management Console.
- Navigate to Billing and Cost Management > Cost Explorer.
- Enable Cost Explorer (activates in 24 hours).
2. Set Up Tags:
- Go to AWS Tag Editor.
- Tag resources (e.g., EC2 instances) with keys like “Team” or “Project.”
- Example:
aws ec2 create-tags --resources i-1234567890 --tags Key=Team,Value=DevSecOps.
3. Configure Cost Allocation Reports:
- In Billing Dashboard, create a Cost and Usage Report (CUR).
- Enable tags in CUR for detailed breakdowns.
4. Integrate with CI/CD:
- Use Infracost in GitHub Actions (see code above).
5. Review Dashboards:
- Access Cost Explorer to visualize costs by tag, service, or region.
Step-by-Step Setup (AWS Example)
- Enable Cost and Usage Report (CUR)
aws ce put-report-definition --report-name "FinOpsReport" \
--time-unit DAILY --format textORcsv --compression ZIP \
--s3-bucket bucket-name --s3-prefix reports/ \
--s3-region us-east-1 --report-versioning CREATE_NEW_REPORT2. Create an Athena Table to Query CUR
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE IF NOT EXISTS cost_usage (
identity LineItemId string,
line_item_usage_account_id string,
line_item_usage_type string,
line_item_unblended_cost double
)
ROW FORMAT SERDE 'org.apache.hadoop.hive.serde2.OpenCSVSerde'
LOCATION 's3://bucket-name/reports/';3. Visualize with Grafana
Create dashboards to monitor service-wise cost.
Connect Athena as a data source.
4. Integrate Cost Checks into CI/CD
Example: Fail build if projected cost exceeds threshold
- name: Check Cost Projection
run: |
python scripts/check_cost.py --threshold=505. Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Optimizing CI/CD Pipelines
A DevSecOps team uses Jenkins for CI/CD. Infracost estimates costs for code changes, identifying oversized EC2 instances before deployment, reducing costs by 20% without affecting performance.
Scenario 2: Security Compliance in Multi-Cloud
A financial services company on AWS and Azure uses CloudHealth to track security-related costs (e.g., WAF, DDoS protection), ensuring PCI-DSS compliance while optimizing redundant services.
Scenario 3: Kubernetes Cost Management
A tech startup on GCP uses KubeCost to allocate Kubernetes costs per namespace, rightsizing pods to save 30% on compute costs.
Industry-Specific Example: Healthcare
A healthcare provider manages HIPAA-compliant cloud workloads. Using Cloudability, they track costs for patient data processing, ensuring cost efficiency and security compliance.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Cost Visibility: Granular insights into cloud spending.
- Collaboration: Aligns finance, engineering, and security teams.
- Optimization: Reduces waste via rightsizing and reserved instances.
- Agility: Supports rapid DevSecOps cycles with cost awareness.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Cultural Resistance: Teams may resist cost accountability.
- Complexity: Multi-cloud environments complicate tracking.
- Tool Costs: Third-party FinOps tools can be expensive.
- Maturity Gap: Only 9% of organizations have mature FinOps practices (per FinOps Foundation).
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips, Performance, Maintenance
- Tag Everything: Enforce tagging for all cloud resources.
- Automate Monitoring: Use nOps for real-time cost alerts.
- Regular Reviews: Conduct monthly cost reviews with stakeholders.
| Automation | Tool |
|---|---|
| Cost budget alerts | AWS Budgets, Azure Cost Management |
| Auto-shutdown dev env | Lambda scripts |
| Report generation | Athena + Scheduled Queries |
| Tag enforcement | Terraform + Sentinel or OPA |
Compliance Alignment, Automation Ideas
- Compliance: Map FinOps KPIs to compliance requirements (e.g., SOC 2).
- Automation: Use AWS Lambda to terminate idle resources:
import boto3
def lambda_handler(event, context):
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
instances = ec2.describe_instances(Filters=[{'Name': 'instance-state-name', 'Values': ['running']}])
for reservation in instances['Reservations']:
for instance in reservation['Instances']:
ec2.stop_instances(InstanceIds=[instance['InstanceId']])8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Aspect | FinOps | Traditional IT Finance | DevOps Cost Tools |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Cloud cost optimization | Fixed IT budget management | Ad-hoc cost monitoring |
| Collaboration | Cross-functional (finance, engineering, security) | Finance-led | Engineering-led |
| Tools | CloudZero, Finout, AWS Cost Explorer | Spreadsheets, ERP systems | Infracost, custom scripts |
| Scalability | Dynamic, cloud-native | Static, on-premises focus | Limited to dev workflows |
Choose FinOps for cloud-centric, collaborative cost management; traditional finance for fixed budgets; or DevOps tools for lightweight, engineering-focused solutions.
9. Conclusion
FinOps empowers DevSecOps by integrating financial accountability into secure, rapid software delivery. As cloud adoption grows, expect AI-driven cost optimization and deeper security integration. Start with the FinOps Foundation’s resources at https://www.finops.org and join their Slack community for collaboration.