1. Introduction & Overview
What is a Cloud Cost Analyst?
A Cloud Cost Analyst is a professional or a set of practices focused on monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing cloud computing costs within an organization. This role involves using tools, strategies, and data analytics to ensure cloud resources are used efficiently, aligning spending with business goals. In the context of DevSecOps, a Cloud Cost Analyst integrates cost management into the software development lifecycle (SDLC), embedding cost-awareness alongside development, security, and operations.
History or Background
Cloud cost analysis emerged as organizations increasingly adopted cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) in the early 2010s. The pay-as-you-go pricing model, while flexible, led to unpredictable costs, prompting the need for specialized roles and tools to manage cloud expenditure. The rise of DevSecOps, which emphasizes integrating security and operations into development, further highlighted the importance of cost optimization as a critical component of efficient cloud operations. Tools like AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management, and third-party platforms like CloudHealth evolved to address these needs.
Why is it Relevant in DevSecOps?
In DevSecOps, where speed, security, and collaboration are paramount, unchecked cloud costs can undermine project success. A Cloud Cost Analyst ensures:
- Cost efficiency: Identifies wasteful spending, aligning resources with project needs.
- Security integration: Ensures cost-saving measures don’t compromise security controls.
- Automation alignment: Integrates cost analysis into CI/CD pipelines for real-time insights.
- Compliance: Supports financial accountability and regulatory requirements in cloud deployments.
This role bridges financial management with technical operations, making it essential for scalable, secure, and cost-effective cloud strategies.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
- Cloud Cost Management: The practice of monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing cloud expenses to maximize value.
- FinOps: A cultural and operational framework integrating financial accountability into cloud operations, often overlapping with Cloud Cost Analyst duties.
- Cost Allocation Tags: Metadata labels applied to cloud resources for tracking and categorizing expenses.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Defining cloud infrastructure through code, enabling cost estimation and optimization.
- CI/CD Pipeline: Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery workflows where cost analysis tools can be integrated for real-time monitoring.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| FinOps | Financial Operations — a discipline to manage cloud spend collaboratively. |
| Showback/Chargeback | Models for cost allocation to teams or departments. |
| Resource Tagging | Adding metadata (owner, environment, cost center) to cloud resources. |
| Rightsizing | Optimizing instance sizes based on utilization. |
| Reserved Instances (RI) | Pre-purchased cloud compute capacity for discount. |
| Spot Instances | Discounted, ephemeral compute capacity — risk of termination. |
| Anomaly Detection | Alerts triggered on unexpected cost patterns. |
How It Fits into the DevSecOps Lifecycle
In DevSecOps, the Cloud Cost Analyst role spans the entire SDLC:
- Plan: Defines cost goals and budgets for projects.
- Code: Uses IaC tools like Terraform to estimate costs before deployment.
- Build: Integrates cost analysis tools (e.g., Infracost) into CI pipelines to flag potential cost overruns.
- Test: Ensures cost-optimization doesn’t compromise security or performance.
- Deploy: Monitors real-time costs during deployment using tools like AWS Cost Anomaly Detection.
- Operate: Continuously optimizes resources, leveraging auto-scaling and reserved instances.
- Monitor: Tracks spending trends and sets budget alerts to maintain cost control.
| Phase | Role of Cloud Cost Analyst |
|---|---|
| Plan | Estimate budget, assign cost per feature or service. |
| Develop | Integrate cost feedback in pull requests or commit checks. |
| Build/Test | Evaluate cost of ephemeral test environments. |
| Release | Monitor costs during blue-green or canary deployments. |
| Operate | Track real-time usage, tag drift, and cost anomalies. |
| Monitor | Alerting on cost spikes, auditing for unused or idle resources. |
3. Architecture & How It Works
Components
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Native tools (AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Cost Management) or third-party platforms (CloudHealth, Infracost) for tracking usage.
- Tagging Systems: Metadata for categorizing resources by project, team, or environment.
- Automation Scripts: IaC and CI/CD integrations for proactive cost management.
- Dashboards and Reports: Visualizations for cost trends, forecasts, and anomalies.
- Alerting Systems: Budget alerts and anomaly detection for real-time cost control.
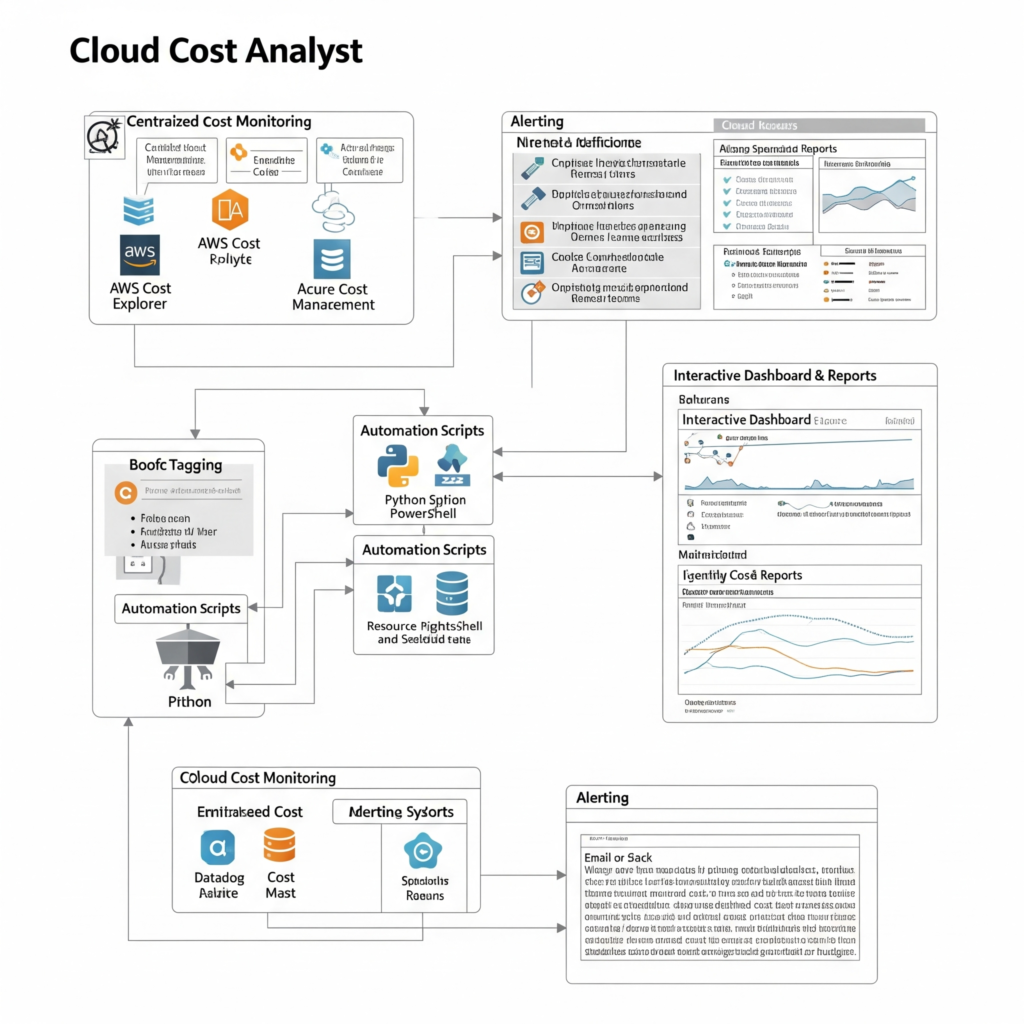
Internal Workflow
- Data Collection: Aggregates usage data from cloud providers.
- Analysis: Processes data to identify cost drivers, underutilized resources, or anomalies.
- Optimization: Recommends actions like right-sizing instances or using reserved instances.
- Reporting: Generates dashboards and reports for stakeholders.
- Automation: Integrates with CI/CD pipelines to enforce cost policies.
Architecture Description
Imagine a layered architecture:
- Data Layer: Cloud provider APIs (e.g., AWS Billing API) feed usage data.
- Processing Layer: Tools like CloudHealth process data, applying tags and cost allocation logic.
- Integration Layer: CI/CD tools (e.g., Jenkins, GitLab) embed cost checks using plugins like Infracost.
- Presentation Layer: Dashboards (e.g., Azure Cost Management) display trends and alerts.
- Security Layer: Ensures cost optimizations align with security policies (e.g., no public S3 buckets to save costs).
[Cloud Provider Billing APIs]
|
[Data Collectors] -----> [Storage Layer (e.g., S3/BigQuery)]
|
[Normalization Engine]
|
-----------------------------
| | |
[Analytics] [Policy Engine] [Alerting]
| | |
[Dashboards] [CI/CD Plugins] [Email/Slack/Teams]
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- Terraform with Infracost: Estimates costs before applying IaC changes.
- Jenkins/GitLab: Integrates cost analysis in CI/CD pipelines for pre-deployment checks.
- AWS Cost Explorer: Monitors real-time costs post-deployment.
- Vault: Secures cost-related secrets (e.g., API keys) in DevSecOps workflows.
4. Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Cloud Account: Access to AWS, Azure, or GCP with billing permissions.
- Tools: Install Infracost, AWS CLI, or Azure CLI.
- Environment: A development environment with Python or Node.js for scripting.
- IAM Permissions: Policies allowing access to cost reports (e.g.,
Allow group <group_name> to read usage-report in tenancy).
Hands-on: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
This guide sets up Infracost with Terraform for cost analysis in a DevSecOps pipeline.
- Install Infracost:
# On macOS
brew install infracost
# On Linux
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/infracost/infracost/master/scripts/install.sh | sh2. Set Up Terraform:
Ensure Terraform is installed and configured with your cloud provider credentials.
3. Create a Sample Terraform File:
provider "aws" {
region = "us-east-1"
}
resource "aws_instance" "example" {
ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0"
instance_type = "t2.micro"
}4. Run Infracost:
infracost breakdown --path .This outputs estimated monthly costs for the Terraform configuration.
5. Integrate with CI/CD (e.g., GitHub Actions):
name: Cost Analysis
on: [push]
jobs:
cost-analysis:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Infracost
run: curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/infracost/infracost/master/scripts/install.sh | sh
- name: Run Infracost
run: infracost breakdown --path . --format json > infracost.json6. Verify Output:
Check the CI/CD pipeline logs for cost estimates and adjust resources if needed.
5. Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Optimizing CI/CD Pipeline Costs
A DevSecOps team uses Infracost in their Jenkins pipeline to estimate costs for each infrastructure change. By identifying over-provisioned EC2 instances, they reduced costs by 20% without impacting performance.
Scenario 2: Multi-Cloud Cost Management
A healthcare organization uses CloudHealth to manage AWS and Azure costs. Tagging resources by department enabled them to allocate costs accurately, ensuring compliance with HIPAA regulations.
Scenario 3: Security-Driven Cost Optimization
A financial services firm integrates cost analysis with security scans in their GitLab CI/CD pipeline. Using tools like tfsec, they ensure cost-saving measures (e.g., downsizing instances) don’t introduce vulnerabilities.
Scenario 4: Scalable Workloads with Auto-Scaling
A SaaS company leverages AWS auto-scaling and reserved instances for non-critical workloads, monitored by a Cloud Cost Analyst. This saved $1.7 million annually while maintaining performance.
6. Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Cost Transparency: Provides clear insights into spending patterns.
- Waste Reduction: Identifies underutilized resources for reallocation or deletion.
- Automation: Integrates with CI/CD for proactive cost control.
- Compliance Support: Aligns with financial and regulatory requirements.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Complexity: Multi-cloud environments require advanced tools and expertise.
- Tool Overlap: Native and third-party tools may duplicate functionality.
- Learning Curve: Requires understanding of cloud pricing models and DevSecOps workflows.
- Security Trade-offs: Cost optimizations may inadvertently weaken security if not carefully managed.
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
- Security Tips:
- Performance:
- Maintenance:
- Regularly review tagging strategies to ensure accurate cost allocation.
- Schedule automated cost reports for ongoing monitoring.
- Compliance Alignment:
- Align with standards like GDPR or HIPAA by tagging sensitive resources.
- Use compliance-as-code tools to enforce cost policies.
- Automation Ideas:
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Tool/Approach | Cloud Cost Analyst (Role/Practices) | AWS Cost Explorer | CloudHealth | Infracost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Holistic role integrating cost, security, and DevSecOps | Native AWS tool for cost analysis | Multi-cloud cost management | IaC-focused cost estimation |
| Integration | CI/CD, IaC, security tools | Limited to AWS CI/CD | Broad CI/CD and multi-cloud | Terraform, GitHub Actions |
| Security Focus | High, aligns with DevSecOps | Low, cost-focused | Moderate, some security features | High, with tfsec integration |
| Ease of Use | Requires expertise | User-friendly | Moderate learning curve | Developer-friendly |
| Best For | Comprehensive DevSecOps cost management | AWS-only environments | Multi-cloud enterprises | IaC-driven teams |
When to Choose Cloud Cost Analyst Role:
- For organizations needing a dedicated role to integrate cost management with security and DevSecOps.
- When operating in complex, multi-cloud environments requiring holistic oversight.
- If embedding cost checks into CI/CD pipelines is a priority.
9. Conclusion
The Cloud Cost Analyst role is pivotal in DevSecOps, ensuring cost efficiency without compromising security or performance. By leveraging tools like Infracost, CloudHealth, and native cloud platforms, analysts can optimize spending, enhance transparency, and align with compliance requirements. Future trends may include AI-driven cost predictions and tighter integration with DevSecOps pipelines. To get started, explore official documentation and communities: